Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Tips for a Happier Gut
IBS, or Irritable Bowel Syndrome, is a chronic disorder characterized by abdominal pain, discomfort, and changes in bowel habits. It is a functional gastrointestinal disorder that does not cause permanent damage to the intestines, but can significantly impact a person's quality of life.
Symptoms of IBS can include bloating, diarrhoea, constipation, and alternating bouts of both. The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but factors such as diet, stress, and the gut microbiome may play a role.
Treatment for IBS often involves dietary modifications, stress management techniques, and medications to alleviate symptoms.
More...
Your Bowel habits

The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but it is considered to be a combination of various factors, including abnormal gut motility, increased sensitivity to certain foods, and stress. While there is no cure for IBS, there are ways to manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected.
This includes dietary modifications such as avoiding trigger foods like caffeine and fatty foods, increasing fibre intake, and staying hydrated. Stress management techniques like regular and relaxation exercises can help alleviate symptoms. Sometimes, medication may be prescribed to manage symptoms like constipation or diarrhoea.
Individuals with IBS must work closely with their healthcare provider to develop an individualised treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and concerns. With the right approach, minimising the impact of IBS on daily life and achieving better overall well-being is possible. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder affecting millions worldwide.
It is characterised by abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
The exact cause of IBS remains unknown, perplexing medical professionals and researchers alike. However, they believe it to be a complex interplay of factors, including abnormal gut motility, heightened sensitivity to certain foods, and the impact of stress on the body.
Although there is no definitive cure for IBS, several strategies are available to manage its symptoms effectively and enhance the overall quality of life for those affected.
Dietary modifications form a crucial component of managing IBS symptoms.
Individuals can reduce their discomfort by avoiding trigger foods like caffeine and fatty substances, while increasing their intake of fibre-rich foods and maintaining proper hydration levels. Additionally, incorporating stress management techniques into daily routines can yield promising results.
Regular exercise and relaxation exercises can help alleviate symptoms by mitigating the effects of stress on the body.
Furthermore, medication may be prescribed in specific cases to address particular symptoms, such as constipation or diarrhoea. Individuals with IBS must collaborate closely with their healthcare provider to develop a tailored treatment plan that caters to their unique needs and concerns.
Adopting the right approach and seeking appropriate guidance from healthcare professionals makes it feasible to minimise the impact of IBS on daily life and achieve better overall well-being.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a perplexing enigma in gastrointestinal disorders. Its exact cause continues to elude medical professionals and researchers alike, leaving them with a complex interplay of factors to consider:
- Abnormal gut motility
- Heightened sensitivity to certain foods
- The insidious impact of stress on the body
Although a definitive cure for IBS remains elusive, several strategies exist that can effectively manage its symptoms and enhance the overall quality of life for those affected.
IBS Diet

Dietary modifications play a crucial role in managing IBS symptoms. Individuals can reduce their discomfort significantly by skilfully avoiding trigger foods like caffeine and fatty substances, while simultaneously ramping up the intake of fibre-rich foods and maintaining proper hydration levels.
Moreover, incorporating stress management techniques into daily routines can yield promising results. Regular exercise and relaxation exercises can help alleviate symptoms by mitigating the harmful effects of stress on the body.
Furthermore, medication may be prescribed as part of an individualised treatment plan in specific cases where symptoms such as constipation or diarrhoea become particularly disruptive. Collaboration between individuals with IBS and their healthcare providers is paramount in developing a tailored approach that addresses their unique needs and concerns.
Adopting this multifaceted approach and seeking appropriate guidance from healthcare professionals makes it feasible to minimise the impact of IBS on daily life and achieve better overall well-being.
IBS medication
In irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) patients with diarrhoea, an antidiarrhoeal agent such as loperamide is a drug which slows gut transit.
Side effects include:
- abdominal pain
- constipation, which can become severe.
Secretagogues/Prosecretory agents are a class of drugs which increase fluid secretion and movement in the GI tract.
These drugs also can improve pain, discomfort, and bloating.
Lubiprostone (Amitiza®)
Plecanatide (Trulance®)
Linaclotide (Linzess®)
The possible adverse reactions are diarrhoea.
Retainagogues block the absorption of sodium from food and drink in the GI tract.
Tenapanor (Ibsrela®)
expected side effects noted in clinical trials include diarrhoea, abdominal distension, and flatulence.
Antispasmodics are drugs which suppress smooth muscle contractions in the GI tract.
Some possible side effects are headaches, dry eyes and mouth, blurred vision, rash, mild sedation, or drowsiness.
Medication plays a crucial role in the management of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), especially when specific symptoms like constipation or diarrhoea become particularly disruptive. In such cases, healthcare providers may prescribe medication as part of an individualised treatment plan.
These medications aim to alleviate the symptoms and relieve those affected by IBS. However, it is essential to note that medication alone is not a definitive cure for IBS. It should be used with other strategies, such as dietary modifications and stress management techniques, to achieve optimal results. Working closely with healthcare providers ensures that the prescribed medication aligns with the individual's unique needs and concerns.
By adopting this multifaceted approach and seeking appropriate guidance from healthcare professionals, individuals can minimise the impact of IBS on their daily lives and strive towards better overall well-being.
IBS Bloating
Bloating is a common symptom experienced by individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). It is characterised by a feeling of fullness and distension in the abdominal area, often accompanied by discomfort or pain. The exact cause of bloating in IBS remains unclear. Still, it is thought to be related to abnormal gut motility and increased sensitivity to gas in the digestive system.
Managing bloating in IBS can be challenging, but some strategies can help alleviate symptoms. Dietary modifications are crucial, as certain foods can contribute to bloating. Individuals with IBS should avoid gas-producing foods like beans, lentils, broccoli, cabbage, and carbonated drinks.
Additionally, eating smaller meals more frequently and chewing food thoroughly can aid digestion and reduce the likelihood of bloating.
Regular physical activity in daily routines can promote better digestion and help reduce bloating. Exercise stimulates the movement of the intestines, aiding in the elimination of gas.
Furthermore, stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises or mindfulness meditation can help relax the body and minimise symptoms.
It is vital for individuals with IBS experiencing persistent bloating to consult their healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance on managing this particular symptom.
Working collaboratively with healthcare professionals can lead to a tailored treatment plan that addresses individual needs and concerns, ultimately reducing the impact of bloating on daily life and improving overall well-being.
IBS constipation
Constipation is a prevalent symptom among irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) individuals. It is characterised by infrequent bowel movements and difficulty passing stool. The underlying cause of constipation in IBS is not fully understood. Still, it is thought to be related to abnormal muscle contractions in the intestines and increased sensitivity to pain.
Managing constipation in IBS requires a multifaceted approach. Dietary modifications can be significant, as certain foods can promote or alleviate constipation.
Individuals with IBS should consider increasing their fibre-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, as this can help soften the stool and facilitate regular bowel movements. Maintaining proper hydration levels by drinking adequate water throughout the day is also necessary.
In addition to dietary changes, regular physical activity is essential for promoting healthy digestion and preventing constipation. Exercise stimulates the muscles in the intestines, helping to move waste through the digestive system more efficiently.
Furthermore, stress management techniques can be beneficial, as stress has been known to exacerbate symptoms of constipation. Engaging in relaxation exercises or seeking therapy can help individuals with IBS better cope with stress and reduce its impact on their digestive health.
For individuals experiencing persistent constipation, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance on managing this symptom.
A tailored treatment plan that considers individual needs and concerns can be developed in collaboration with healthcare professionals, ultimately improving overall well-being and minimising the impact of constipation on daily life.
IBS Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is a common and disruptive symptom experienced by individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). It can range from mild discomfort to severe cramping, and its exact cause is not fully understood. However, it is believed to be related to abnormal muscle contractions in the intestines and heightened pain sensitivity.
Managing abdominal pain in IBS requires a comprehensive approach that addresses this symptom's physical and emotional aspects. Dietary modifications can be significant, as certain foods can trigger or exacerbate abdominal pain.
Individuals with IBS should avoid potential triggers such as spicy foods, caffeine, alcohol, and fatty or fried foods.
In addition to dietary changes, stress management techniques are crucial for reducing abdominal pain. Stress has been shown to worsen IBS symptoms, including abdominal pain. Relaxation exercises like deep breathing or mindfulness meditation can help calm the body and alleviate symptoms.
It is vital for individuals experiencing persistent or severe abdominal pain to consult their healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance on managing this particular symptom.
Working collaboratively with healthcare professionals can lead to a personalised treatment plan that addresses individual needs and concerns, ultimately improving overall well-being and minimising the impact of abdominal pain on daily life.
Diet for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
The diet plays a crucial role in managing the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Making certain dietary modifications can help alleviate discomfort and promote overall digestive health.
One of the key aspects of an IBS-friendly diet is identifying and avoiding trigger foods. These foods can exacerbate bloating, constipation, or abdominal pain. Common trigger foods include spicy dishes, caffeine, alcohol, and fatty or fried foods.
In addition to avoiding trigger foods, individuals with IBS should consider incorporating fibre-rich foods into their diet. Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are excellent sources of dietary fibre that can help soften the stool and regulate bowel movements. However, it is necessary to increase fibre intake gradually to avoid worsening symptoms.
Hydration is another crucial aspect of an IBS diet. Drinking adequate water throughout the day helps maintain proper digestion and prevents constipation.
Lastly, some individuals may find it helpful to keep a food journal to track their symptoms and identify any patterns or triggers. This can provide valuable insights into which foods may be causing discomfort.
Individuals with IBS must consult their healthcare provider or a registered dietitian for personalised guidance on implementing dietary changes.
A tailored diet plan can be developed based on individual needs and preferences, ultimately improving overall well-being and quality of life for those with IBS.
IBS Statistics

Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder affecting millions worldwide. It is estimated that 10-15% of the population suffers from IBS, with women being twice as likely to be affected as men.
While the exact cause of IBS is unknown, several factors are acknowledged to contribute to its development, including abnormal muscle contractions in the intestines and heightened sensitivity to pain.
Symptoms of IBS can vary from person to person but often include abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhoea. These symptoms can be disruptive and have a significant impact on daily life. Therefore, individuals with IBS need to seek proper management strategies.
In addition to dietary changes, regular physical activity is essential for promoting healthy digestion and preventing constipation. Exercise stimulates the muscles in the intestines, helping to move waste through the digestive system more efficiently.
Furthermore, stress management techniques can be beneficial, as stress has been known to exacerbate symptoms of constipation.
For individuals experiencing persistent constipation or abdominal pain, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance on managing these specific symptoms.
A tailored treatment plan that considers individual needs and concerns can be developed in collaboration with healthcare professionals, ultimately improving overall well-being and minimising the impact of IBS on daily life.
Understanding and addressing the various aspects of IBS can help individuals better manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Stress Management for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
In addition to dietary changes and regular physical activity, stress management techniques are crucial for reducing abdominal pain associated with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). It has been shown that stress can worsen IBS symptoms, including abdominal pain.
Therefore, relaxation exercises such as deep breathing or mindfulness meditation can help calm the body and alleviate these distressing symptoms. It is crucial for individuals experiencing persistent or severe abdominal pain to consult their healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance on managing this particular symptom.
By working collaboratively with healthcare professionals, a personalised treatment plan can be developed that addresses individual needs and concerns, ultimately improving overall well-being and minimising the impact of abdominal pain on daily life. Taking steps to manage stress alongside other lifestyle modifications can significantly enhance one's ability to cope with IBS and improve their quality of life effectively.
Cause of IBS
Irritable bowel syndrome, commonly known as IBS, is a chronic gastrointestinal disorder affecting millions worldwide. The exact cause of IBS still needs to be fully understood, which adds to the complexity of managing this condition. However, researchers believe that a combination of factors contributes to the developing of IBS.
These factors may include abnormal muscle contractions in the intestines, heightened sensitivity to food and stress, and changes in the gut microbiome. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, and inadequate sleep may also trigger IBS symptoms.
It is important to note that IBS is a multifactorial condition, meaning that no single cause can be pinpointed. Therefore, a comprehensive approach that addresses various aspects of an individual's health and well-being is often necessary to effectively manage IBS to enhance their quality of life.
- Muscle contractions in the intestine. The walls of the intestines are lined with layers of muscle that contract as they move food through your digestive tract. More muscular contractions that last longer than usual can cause gas, bloating and diarrhoea. Weak contractions can slow food passage and lead to hard, dry stools.
- Nervous system. Issues with the nerves in your digestive system may cause discomfort when your abdomen stretches from gas or stool. Poorly coordinated signals between the brain and the intestines can cause your body to overreact to changes typically occurring in the digestive process. This can result in pain, diarrhoea or constipation.
- Severe infection. IBS can develop after a severe bout of diarrhoea caused by bacteria or a virus. This is called gastroenteritis. IBS might also be associated with a surplus of bacteria in the intestines (bacterial overgrowth).
- Early life stress. People exposed to stressful events, especially in childhood, tend to have more symptoms of IBS.
- Changes in gut microbes. Examples include changes in bacteria, fungi and viruses, which typically reside in the intestines and play a key role in health. Research indicates that the microbes in people with IBS might differ from those in people who don't have IBS.
Triggers for Irritable Bowel Syndrome

Several triggers can exacerbate symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). These triggers include certain foods, stress, and hormonal changes. Identifying and avoiding trigger foods can be vital in managing symptoms for many individuals with IBS.
Common trigger foods include spicy or fatty foods, caffeine, alcohol, and artificial sweeteners.
It is also important to note that everyone's triggers may differ, so it may require trial and error to determine which foods worsen symptoms. In addition to dietary triggers, stress impacts IBS symptoms significantly.
Stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises and mindfulness meditation can help alleviate abdominal pain and discomfort. Lastly, hormonal changes, particularly in women during their menstrual cycle, can also contribute to flare-ups of IBS symptoms.
Understanding these triggers and implementing strategies to minimise their impact can significantly improve the overall management of IBS.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a complex condition with numerous potential triggers that can exacerbate symptoms. These triggers include certain foods, stress, and hormonal changes. Identifying and avoiding trigger foods is crucial for many individuals in effectively managing their IBS symptoms.
Spicy or fatty foods, caffeine, alcohol, and artificial sweeteners are commonly known as trigger foods, although it's important to note that everyone's triggers may differ. Therefore, some trial and error may be necessary to pinpoint specific foods that worsen symptoms.
Stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises and mindfulness meditation can relieve abdominal pain and discomfort associated with IBS.
Moreover, hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle can also contribute to flare-ups of IBS symptoms in women. By understanding these triggers and implementing strategies to minimise their impact, individuals can significantly improve their overall management of IBS and enhance their quality of life.
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis
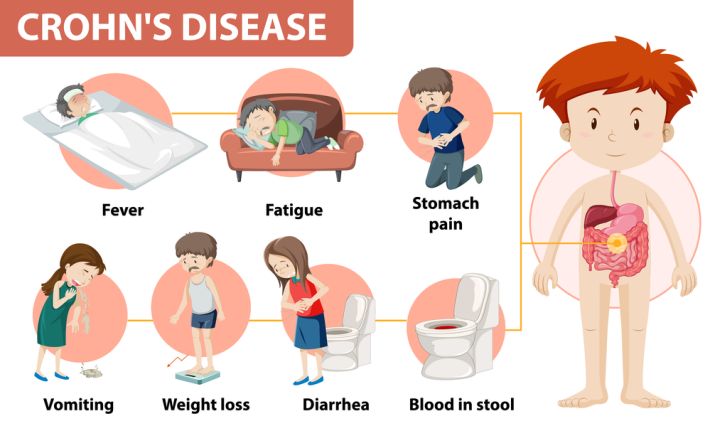
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are the two primary forms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus.
It can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhoea, fatigue, and weight loss. On the other hand, ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the colon and rectum. It causes symptoms similar to Crohn's disease, including abdominal pain, diarrhoea, and fatigue.
While both conditions share some similarities, they also have distinct differences in the areas of the digestive tract they affect and the specific symptoms they present. It is important to note that Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are chronic conditions requiring ongoing management and treatment.
IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) and IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease) are two different gastrointestinal disorders. The main difference is that IBS is a functional disorder, while IBD is a chronic inflammatory condition.
IBS is characterised by recurring symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhoea, but it does not cause any structural damage to the digestive tract. On the other hand, IBD refers to a group of inflammatory conditions, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, which cause inflammation and damage to the gastrointestinal tract.
If left untreated, IBD often requires long-term medical treatment and can result in serious complications. While IBS and IBD can have similar symptoms, the underlying causes and treatment approaches differ significantly.
Conclusion: Tips for a Happier Gut
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, gas, constipation, and diarrhoea. Living with IBS can be challenging and can significantly impact a person's quality of life. However, there are steps you can take to manage the symptoms and improve your gut health. Here are some tips for a happier gut:
1. Identify Trigger Foods:
One of the primary ways to manage IBS is to identify and avoid trigger foods. These are foods that can worsen your symptoms. Common trigger foods include high-fat foods, spicy foods, caffeine, alcohol, and artificial sweeteners. Keeping a food diary can help you identify which foods are causing your symptoms, allowing you to make necessary adjustments to your diet.
2. Eat a Balanced Diet:
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for managing IBS symptoms. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your meals. These foods are rich in fibre and can help regulate your bowel movements. It's also important to drink enough water throughout the day to stay hydrated.
3. Practice Mindful Eating:
Mindful eating involves paying attention to your body's hunger and fullness cues, as well as the taste and texture of the food. It can help prevent overeating and aid in digestion. Take your time when eating, chew your food thoroughly, and avoid distractions such as watching TV or using your phone.
4. Manage Stress:
Stress can exacerbate IBS symptoms, so it's crucial to find healthy ways to manage stress. Engaging in regular exercise, practising relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation, and getting enough sleep can all help reduce stress levels. It may also be beneficial to explore activities that you enjoy, such as hobbies or spending time with loved ones.
5. Stay Active:
Regular physical activity can play a significant role in managing IBS symptoms. Exercise helps stimulate bowel movements and reduces overall stress levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, most days of the week.
6. Consider Probiotics:
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help restore the balance of gut flora. They may provide relief from some IBS symptoms. Talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian to determine if probiotic supplements or foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt or kefir, are right for you.
7. Seek Professional Help:
If you're struggling with managing your IBS symptoms, don't hesitate to seek professional help. A healthcare provider, such as a gastroenterologist or registered dietitian, can provide guidance and develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Living with IBS can be challenging, but by implementing these tips and making lifestyle changes, you can improve your gut health and achieve a happier gut. Remember to be patient with yourself and seek support when needed.

