Common Skin Disorders

Being the largest organ of the human body, your skin is subject to any number of health risks. Your skin provides the initial defense against infection and disease, as it is one of the many components of your immune system. Young and old alike can expect some type of skin problem, large or small, in their lifetime.
More...
Young and old alike can expect some type of skin problem, large or small, in their lifetime. The following are the 5 most common skin disorders, in many cases preventable and always treatable.
Acne
Most acne cases are experienced between the ages of 12 and 30. The largest grouping of occurrences is in the preteen and teen years.
Acne and pimples usually develop on the face, shoulders, chest, back and neck, though this skin disease can pop up anywhere.
Acne occurs when your hair follicles become clogged and a small bump is raised on your skin, called a pimple.
Acne is not a serious physical health concern.
However, acne both mild and severe can lead to a person withdrawing from society and experiencing low levels of self-esteem.
It is thought that acne is most active during the teen and preteen years because this is a period of hormonal upheaval.
As new hormones are produced, and a growth spurt occurs, excess oil development can cause follicles to become stopped up, and acne can develop.
- Commonly located on the face, neck, shoulders, chest, and upper back
- Breakouts on the skin composed of blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, or deep, painful cysts and nodules
- May leave scars or darken the skin if untreated
Acne is treatable in every case.
When it is experienced in the preteen and teen years, it often disappears after a few years. Topical creams and applications both prescribed and over-the-counter are the most common treatment methods.
In severe cases, lifelong scarring may occur.

Eczema
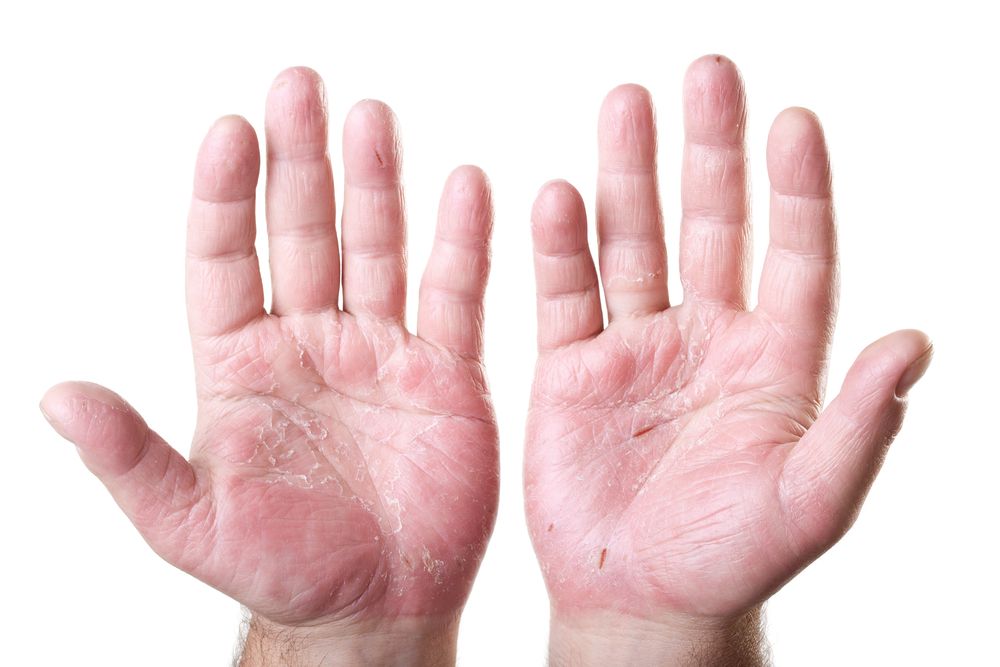
Eczema is a common skin condition marked by itchy and inflamed patches of skin. It’s also known as atopic dermatitis. It is more common in babies and young children, and often occurs on the faces of infants.
It also often appears inside the elbows and behind the knees of children, teenagers, and adults.
In rare cases, atopic dermatitis can first appear during puberty or adulthood. It affects males and females equally.
Itchy, red, dry skin caused by inflammation could be a sign of eczema. Eczema is actually a medical term used to identify a group of conditions that cause the skin to become irritated.
The most common of these conditions is Atopic Dermatitis, also called Atopic Eczema.
Other types include:
- Contact dermatitis is caused by contact with irritants. Burning, itching, and redness occur. The inflammation goes away when the irritant is removed.
- Dyshidrotic dermatitis affects fingers, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet. It causes itchy, scaly patches of skin that flake or become red, cracked, and painful. The condition is more common in women.
- Nummular dermatitis causes dry, round patches of skin in the winter months. It usually affects the legs. It is more common in men.
- Seborrheic dermatitis causes itchy, red, scaly rashes, particularly on the scalp, on the eyebrows, on the eyelids, on the sides of the nose, and behind the ears.
Many times, when eczema is present, this skin disorder is a warning sign that allergic conditions like hay fever and asthma will develop as well.
Eczema is nearly always itchy, and an itching sensation in a, focused part of your skin will begin before a physical rash appears.
The rash is most common on the backs of the knees, the wrists or the hands, the feet or the face, though eczema can attack anywhere on your body, it is not contagious and becomes less severe with age.
Your skin will appear dry, thick and scaly, and the cause of eczema is not known. Medical treatment seeks to prevent and relieve itching, which can lead to infection and other health problems.
Creams and lotions are available to treat eczema, and you should also avoid irritants to the affected area.


Seborrheic Dermatitis
Sometimes called seborrhea, this is a very common skin disease. It causes an itchy, red rash with white scales. Seborrheic dermatitis is known as cradle cap when it occurs in infants, and adults are not immune. If you avoid this skin disorder as a child, it usually doesn't pop up until you are between the ages of 30 and 60.
Men develop seborrhea more frequently than women, and if you have oily skin your risk rises. Dermatologists believe it may be caused by stress, genetic disposition, a yeast which lives on your skin, cold, dry weather and specific medical conditions and medicines.
Skin Cancer
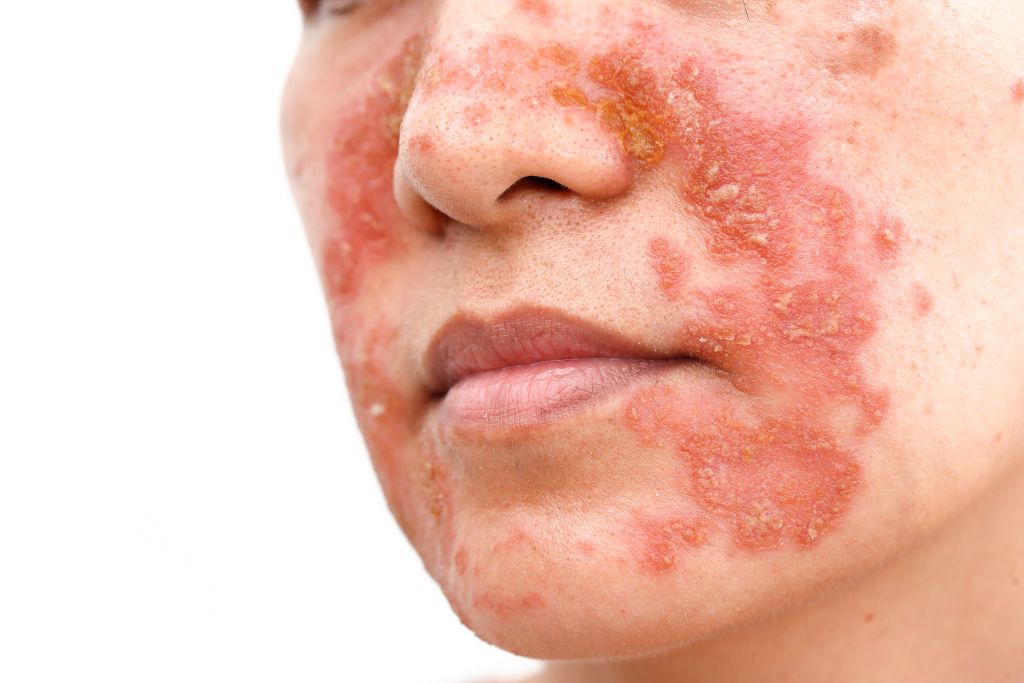
Melanoma is the most dangerous skin cancer, though it is only the third most common type. Melanoma can spread when not detected early, but when it is found in its earliest stages it is most often curable. The most consistent cause of melanoma, and many other skin cancers, is overexposure to the sun.
Melanoma kills between 50,000 and 100,000 people worldwide each year, so if you see a discolored spot or bump on your skin, have it checked out.
Basal Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma are the two most common types of skin cancer, also frequently caused by too much exposure to the sun.

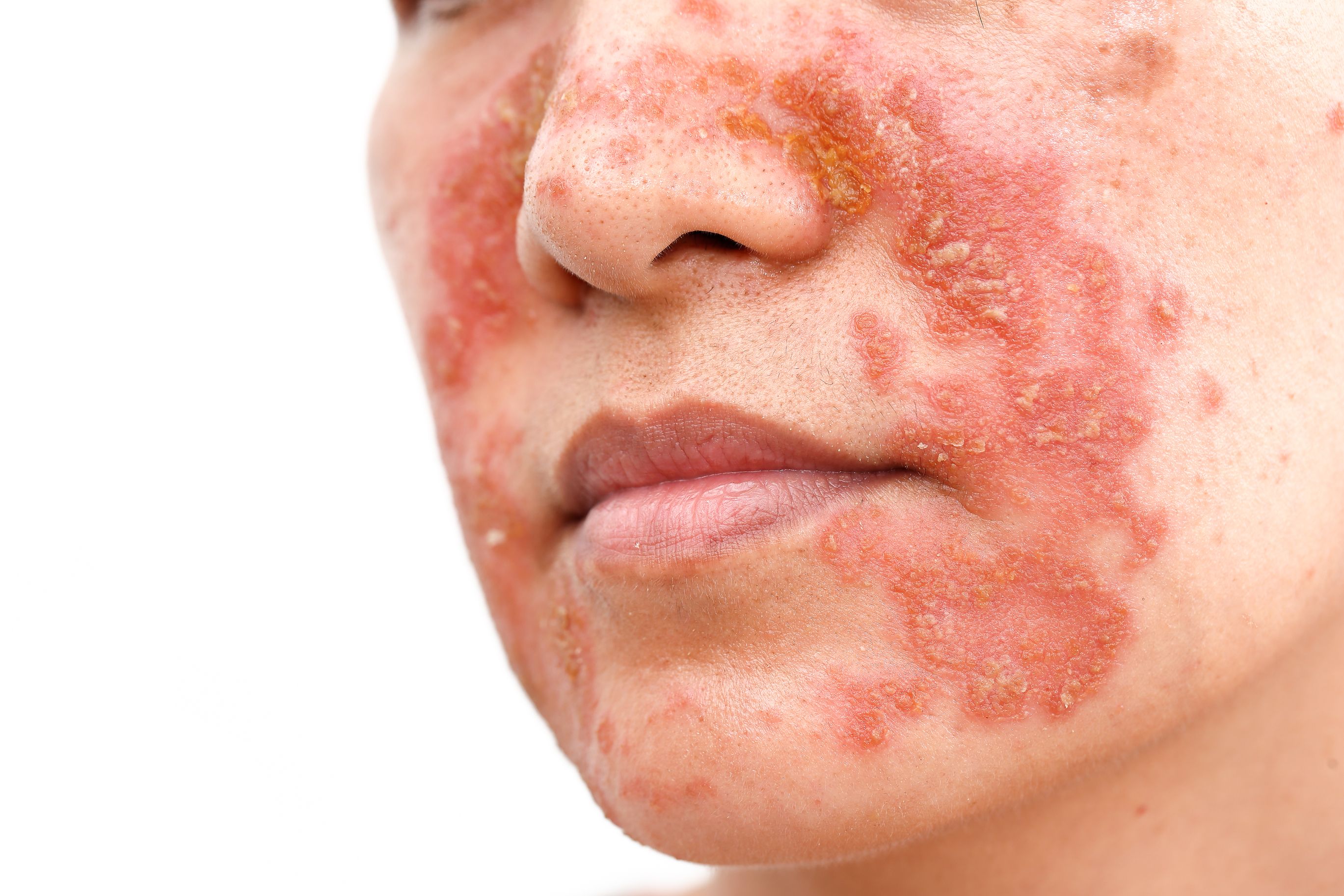
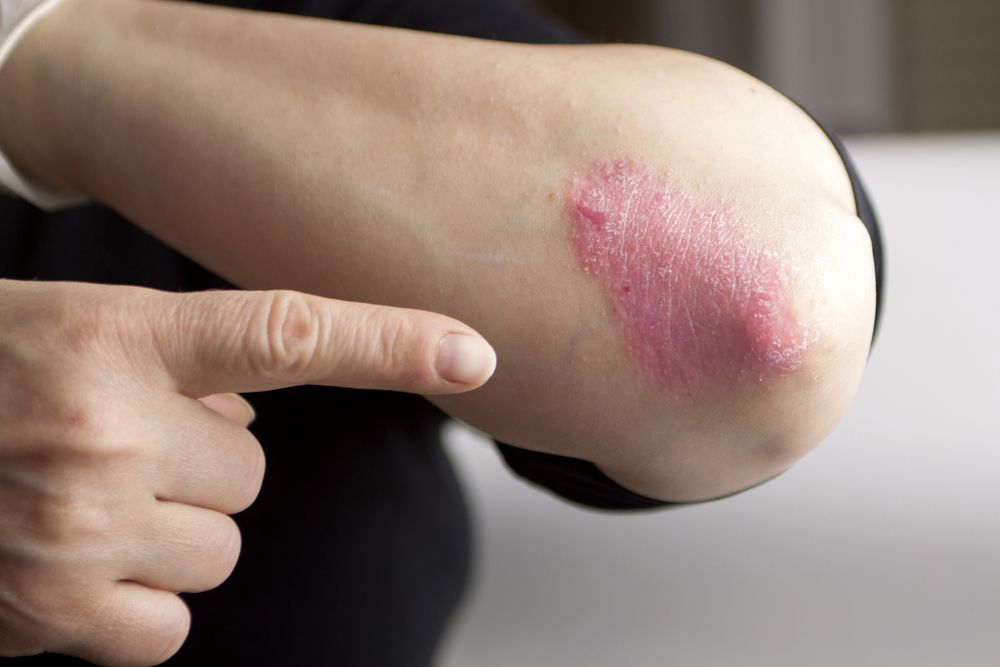
Psoriasis
Psoriasis a common and chronic skin condition. It occurs when your immune system is overactive, and appears as thick, flaky, red or silver patches of skin. What happens is some of your skin cells begin to grow roughly 5 times faster than normal.
The exact reason for psoriasis is unknown, but there are simple and effective treatment methods. Light therapy, oral medications and steroid creams are common treatment protocols.
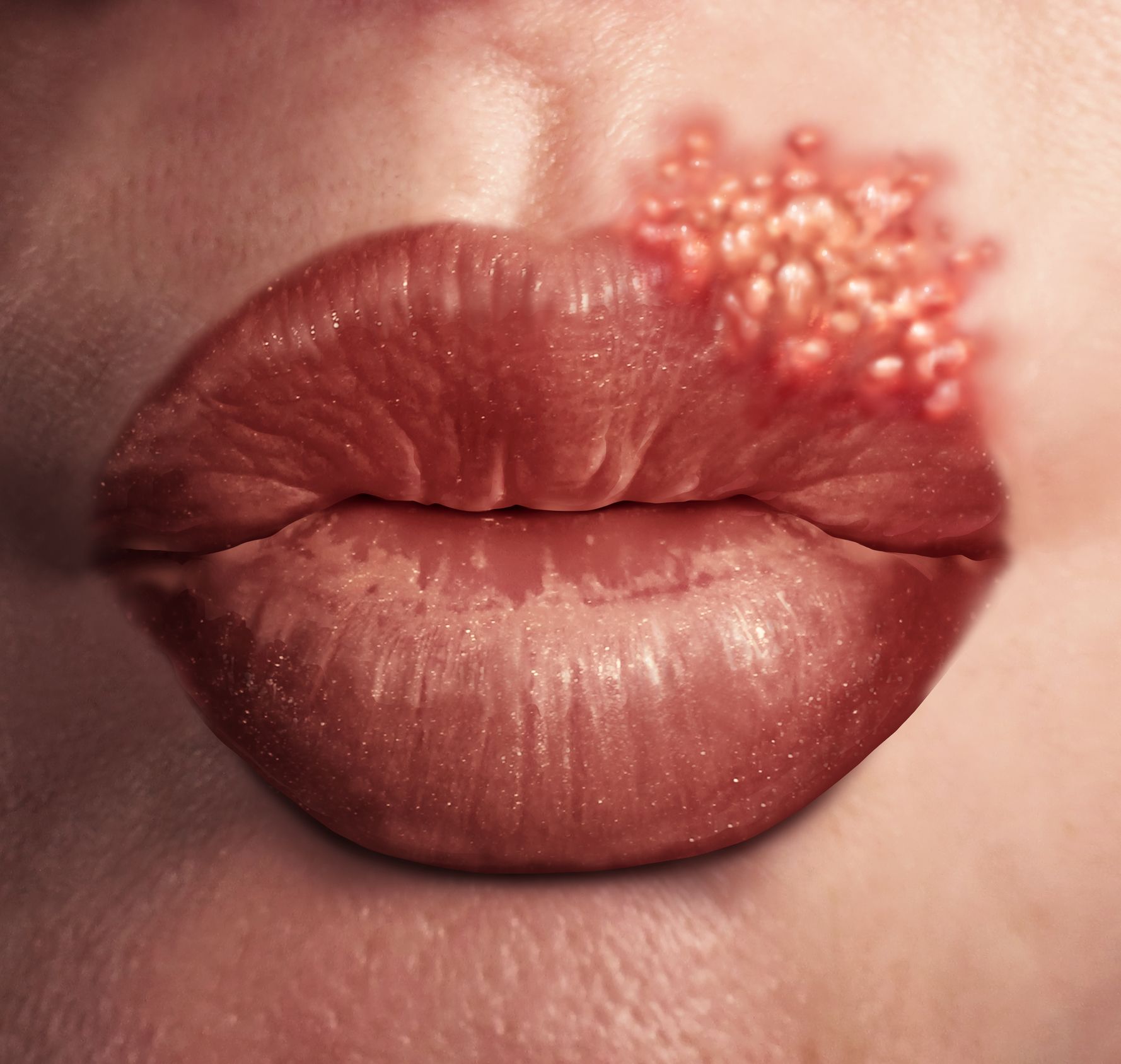
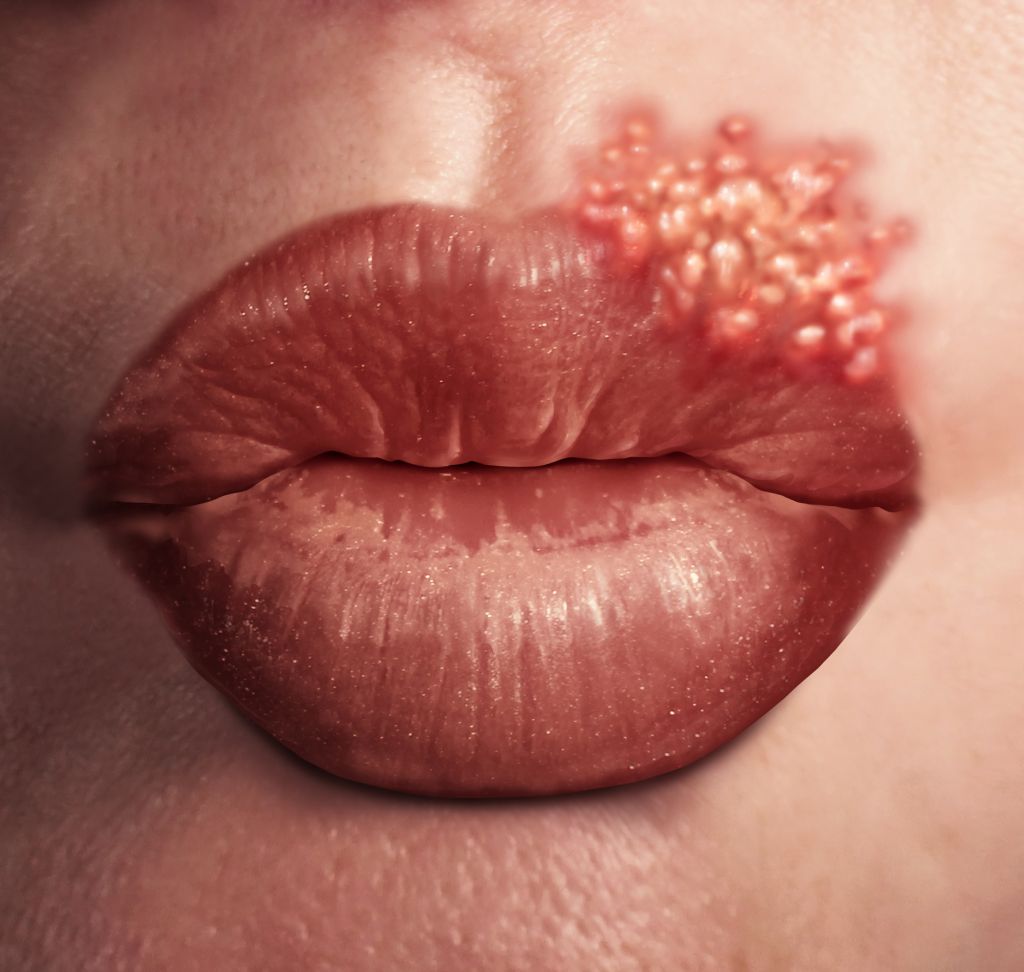
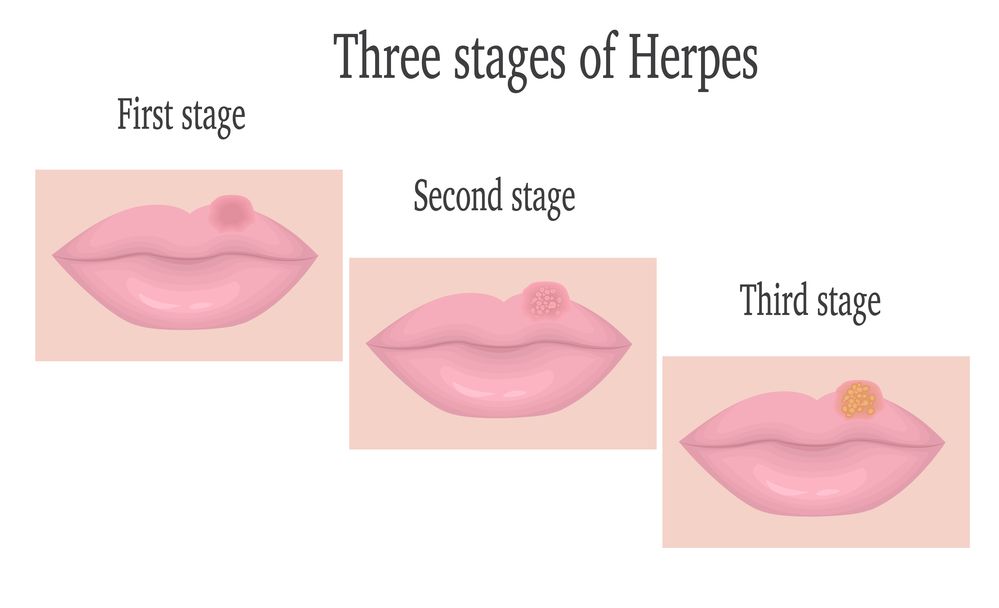
Cold sores
Cold sores are red, fluid-filled blisters that form near the mouth or on other areas of the face. In rare cases, cold sores may appear on the fingers, nose, or inside the mouth. They’re usually clumped together in patches. Cold sores may persist for two weeks or longer.
A common virus called herpes simplex causes cold sores. They can spread from person to person through close contact, such as kissing. The sores are contagious even when they’re not visible.
- Red, painful, fluid-filled blister that appears near the mouth and lips
- Affected area will often tingle or burn before the sore is visible
- Outbreaks may also be accompanied by mild, flu-like symptoms such as low fever, body aches, and swollen lymph nodes
There’s no cure for cold sores, and they may return without warning.
Certain medications can be used to treat cold sores and prevent them from coming back.
Cold sores are caused by the herpes simplex virus.
There are two types of the herpes simplex virus.
The herpes simplex type 1 virus (HSV-1) usually causes cold sores, and the herpes simplex type 2 virus (HSV-2) usually causes genital herpes.
The actual sores are similar in appearance for both forms of the virus. It’s also possible for HSV-1 to cause sores on the genitals and for HSV-2 to cause sores on the mouth.
Visible cold sores are contagious, but they may be spread even when they can’t be seen.
You can get the herpes simplex virus by coming in contact with infected individuals.
This may happen through kissing, sharing cosmetics, or sharing food.
Oral sex may spread both cold sores and genital herpes.

Shingles
The Varicella-Zoster virus that also causes chickenpox may cause shingles as well. After a person has chickenpox, the varicella zoster virus that causes it remains in the body in an inactive state. The virus can reactivate years later, which causes a disease called shingles.
more Information on chickenpox and Shingles
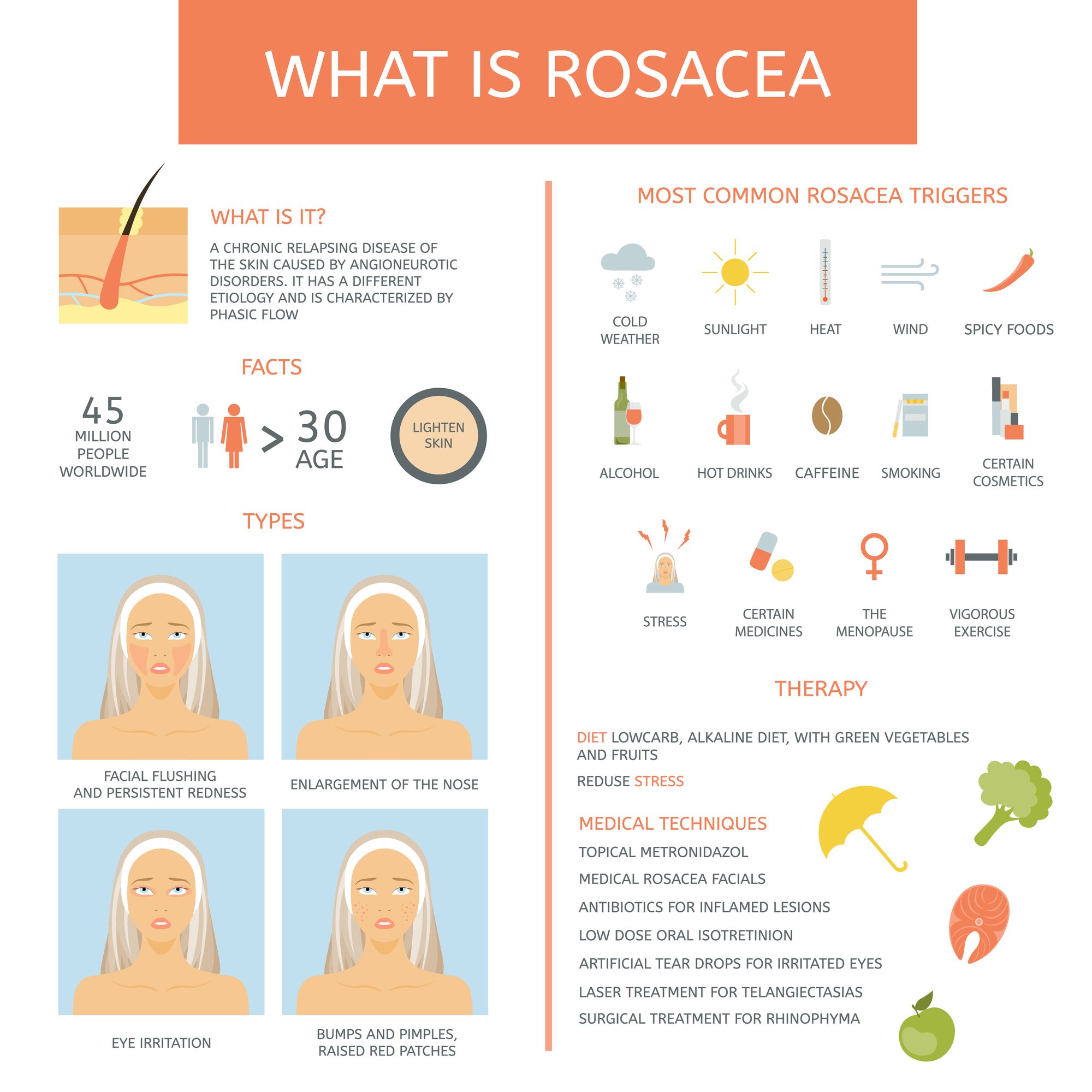
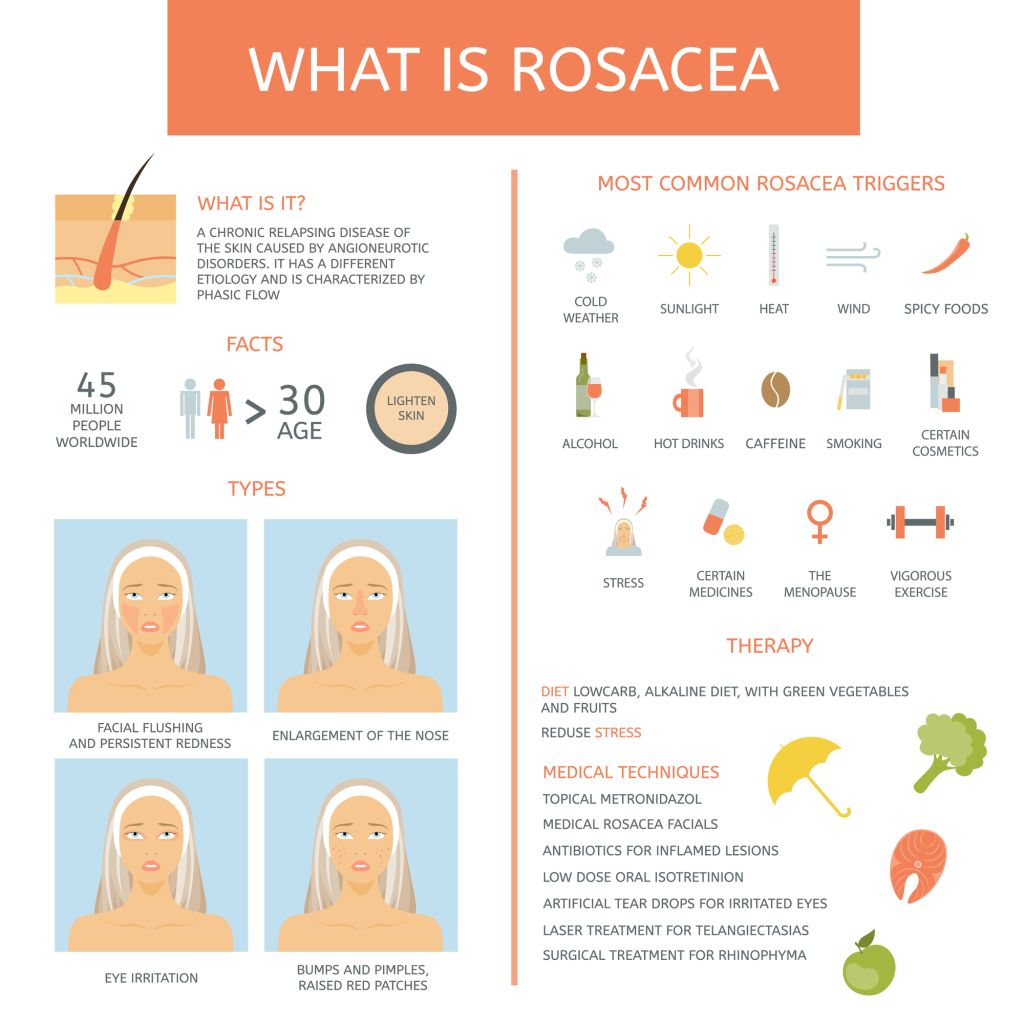
Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic skin disease that affects more than 16 million Americans. The cause of rosacea is still unknown, and there is no cure. However, research has allowed doctors to find ways to treat the condition by minimizing its symptoms.
There are four subtypes of rosacea.
Each sub type has its own set of symptoms.
It is possible to have more than one sub type of rosacea at a time.
Rosacea’s trademark symptom is small, red, pus-filled bumps on the skin that are present during flare-ups.
Typically, rosacea affects only skin on your nose, cheeks, and forehead.
Flare-ups often occur in cycles.
This means that you will experience symptoms for weeks or months at a time, the symptoms will go away, and then return.
What causes rosacea
The cause of rosacea has not been determined. It may be a combination of hereditary and environmental factors.
It is known that some things may make your rosacea symptoms worse.
These include:
- eating spicy foods
- drinking alcoholic beverages
- having the intestinal bacteria Helicobacter pylori
- a skin mite called demodex and the bacterium it carries, Bacillus oleronius
- the presence of cathelicidin (a protein that protects the skin from infection)
Ringworm
Ringworm, also known as dermatophytosis or tinea, is a fungal infection of the skin.
The name “ringworm” is a misnomer, since the infection is caused by a fungus, not a worm.
Ringworm infection can affect both humans and animals.
The infection initially presents with red patches on affected areas of the skin and later spreads to other parts of the body.
The infection may affect the skin of the scalp, feet, groin, beard, or other areas.
Ringworm can go by different names depending on the part of the body affected.
- Ringworm of the scalp (tinea capitis) often starts as small sores that develop into itchy, scaly bald patches. It is most common among children.
- Ringworm of the body (tinea corporis) often appears as patches with the characteristic round “ring” shape.
- Jock itch (tinea cruris) refers to ringworm infection of the skin around the groin, inner thighs, and buttocks. It is most common in men and adolescent boys.
- Athlete’s foot (tinea pedis) is the common name for ringworm infection of the foot. It is frequently seen in people who go barefoot in public places where the infection can spread, such as locker rooms, showers, and swimming pools.
Three different types of fungi can cause this infection.
They are called trichophyton, microsporum, and epidermophyton.
It’s possible that these fungi may live for an extended period as spores in soil. Humans and animals can contract ringworm after direct contact with this soil.
The infection can also spread through contact with infected animals or humans.
The infection is commonly spread among children and by sharing items that may not be clean.
Anyone can develop ringworm. However, the infection is very common among children and people who own pet cats. Both cats and dogs can catch ringworm and then pass it on to humans who touch them. Signs to be aware of in pets include:
- hairless patches of skin that appear circular
- crusty or scaly patches
- patches that may not be completely hairless but have brittle or broken hairs
- opaque or whitish areas around the claws
You may be more likely to develop dermatophytosis if you come into contact with the fungi while you’re wet or if you have minor skin injuries or abrasions. Using a public shower or public pool areas may also expose you to the infective fungi.
If you’re often barefoot, you may develop ringworm of the feet (athlete’s foot). Those who often share items such as hairbrushes or unwashed clothing also have an increased risk of developing the infection.
https://www.healthline.com/health/ringworm#risk-factors
All skin conditions should be referred to a physician for examination and treatment. A macule is a change in surface color without elevation or depression.
They come in various sizes, usually 5-10 millimeters in diameter.
They are most common on the back, chest, arms, and face. They can be hypopigmented or hyperpigmented skin tissue.
A birthmark may be considered if it is small.
Rashes may also be considered if the color of the rash is varied from the skin, for example in café au lait spots.
If they're lesions, they may spread.
Vitiligo is a disease that causes the loss of skin color in blotches.
This may also include skin cancers, or ultraviolet light exposures, also called age spots.
A papule is an area of abnormal skin tissue. There are typically less than 1 centimeter, they have distinct borders, and come in a variety of shapes.
They may have skin lesions and essentially are changes in the skin color or texture of your skin.
Papules can cluster together to form a rash.
They are caused by a number of skin conditions most commonly dermatitis, chicken pox, and eczema.
They can be relieved with home treatments.
Papules appear sometimes with new medication and you should consult your doctor. A papule may also appear from a tick bite; you need to consult the doctor to determine if you have Lyme disease.
A nodule is a growth of forms under the skin.
They may be filled with inflamed tissue or a mix of tissue and fluid.
They may have colored fluid within the nodule which may indicate an infection.
Inflamed tissues that collect together may form a lump. They can grow within any level of the skin, either the subcutaneous layer, the dermal, or the epidermal layer.
There are sometimes found on the body's organs as well. They range in size, they can be cancerous or non-cancerous, but most are benign.
Common areas for nodules include the thyroid glands, lungs, underarms, and groin.
A tumor is any mass lesion or abnormal growth of body tissue. It's generally larger than a nodule. It may either be malignant, cancerous, or benign (non-cancerous) signs and symptoms include weight loss, persistent headaches, chronic fatigue, nausea, and vomiting.
Different things that can affect the modes of transmission of tumors include diet, genetics, which include a family history, the environment, excessive sunlight exposure, obesity, and radiation.
Some tumors are more common in one gender than another. A plaque is a usually well circumscribed lesion with a large surface area and slight elevation.
Signs and symptoms include red and scaly skin, crusting of the scalp, discoloration the fingernails.
Causes or transmission of the disease include stress or trauma from streptococcal infections, abnormality to immune systems, certain medications and drugs may aggravate the condition, this may also be genetic.
A wheal is an elevation of the skin with smooth surfaces, sloping borders, and light pink coloring.
They're caused by acute areas of edema in the skin.
They may appear, disappear, or change form abruptly within hours or minutes. Their size ranges from three to twenty centimeters.
Signs and symptoms may be an allergic reaction, they're typically red or pink in color, smooth elevations around the surrounding skin.
Itchiness or irritation may occur; they may occur frequently or unpredictably.
The mode of transmission for a wheal is pain medication, scratching, temperatures either too hot or too cold, stress, sunlight, and sometimes exercise. A vesicle is a raised lesion less than 1 centimeter in diameter.
They are typically filled with clear fluid. Signs and symptoms may include allergic reactions to drugs, atopic dermatitis or eczema, autoimmune disorders, chicken pox, poison ivy, herpes simplex, or shingles.
For the mode of transmission, they are possibly contagious when the blisters pop and may spread to other areas.
A bulla is a large blister on the skin; it's often filled with clear fluid.
Signs and symptoms include insect bites, infections, burns, the herpes simplex virus, or allergic skin reactions.
Mode of transmission is very similar. It may be contagious if they break open and leak on the surrounding skin tissue.
A pustule is a small pus filled sac. It's commonly seen in acne; this is an infection on the skin.
Signs and symptoms include chicken pox, yeast infection, and a herpes viral infection, such as cold sores, or genital herpes.
The mode of transmission may also be contagious if they break open and leak on the surrounding skin.
An erosion is a loss of some or all of the epidermis or the outer layer of the skin.
The signs and symptoms include eating away of the surface layer by chemical or physical process such as inflammation. The mode of transmission is not contagious, so if somebody has an erosion you are not likely to catch it from them.
An ulcer is a sore on the skin or mucous membrane; it is a disintegration of tissue.
It can result in a complete loss of the epidermis, and often portions of the dermis, and even subcutaneous fat.
The signs and symptoms of ulcers is they appear is open craters, often round, with layers of skin that have eroded.
The skin around the ulcer may be red, swollen, and tender.
Patients may feel pain on the skin around the ulcer and fluid may ooze from the ulcer.
The mode of transmission for ulcers may be contagious if they're oozing.
A fissure is a crack in the skin, it is most commonly the result of skin dryness.
Ichthyosis is a genetic disorder where there's often severe skin cracking.
Signs and symptoms are linear like cleavages of the skin, sometimes defined as extending into the dermis. They're smaller than skin lacerations, a fissure is not contagious, and there is no mode of transmission.
Atrophy of the skin is a thinning of the upper layer of the skin, which is often caused by aging or topical steroids.
Signs and symptoms of atrophy include tension or tightness of the skin, pain, pitting, dryness, or a papery texture of the skin.
Again atrophy is not contagious and there is no mode of transmission.
Excoriation or neurotic excoriation are skin lesions produced by repetitive scratching.
There is no known underlying physical pathology.
Patients dig at their skin to relieve itching, to extract imaginary objects that they believe are embedded or extruding from the skin.
Signs and symptoms include clear, linear erosions, scabs and scars that are hypopigmented or hyperpigmented.
All lesions are usually of similar size and shape.
Common sites include exterior surfaces the extremities, the face, and the upper back.
There is no mode of transmission and excoriation is not contagious.
A crust or scab is serum, blood, or purulent exudate which dries and is a hallmark of a pyogenic.
Signs and symptoms of a crust can be yellow when they have arisen from dried serum, green or yellow-- signs and symptoms of crusts can be yellow when they have arisen from dried serum, green or yellow-green when formed from purlin exudate, brown or dark-red when form from blood, and the mode of transmission is none,
so these are not contagious either.
A scale is dry, itchy, or red flaky skin.
Signs and symptoms include that dry itchy or red flaky skin; they can look like fish scales or alligator skin.
Associated conditions are psoriasis, dermatitis, eczema and ichthyosis which is fish-scale disease.
Scales are not contagious and therefore do not have a mode of transmission.
Lichenification is a thickening of the skin due to continuous scratching or rubbing.
The skin will have a leathery appearance and is associated with skin conditions in which the skin is continuously irritated, such as eczema.
There is no mode of transmission and lichenification is not contagious.
A scar is a patch of skin that grows over a wound.
It forms after the body heals itself from cuts, scrapes, and burns.
It can also be caused by surgery, chicken pox, acne, and tuberculosis test.
Scars, too, are not contagious, and therefore do not have a mode of transmission.
A keloid is a growth of excessive scar tissue in which the skin is healed after an injury.
Signs and symptoms may include areas that may be flesh colored, pink, red, or purple.
A lumpy rigid area skin, itchy patches of skin, and the scar tissue may continue to grow larger over a period of time.
Keloids are not contagious, but the exact cause is unknown and maybe most common in darker skin toned people.
Due to injury, either avulsion or surgical trauma and piercing. Uticaria is also known as hives.
They are raised, often itchy, red welts on the surface of the skin. It's usually an allergic reaction to food or medicine.
Signs and symptoms include slightly raised pink or red swelling on the skin, welts that occur alone or in a group or connect over a large area, skin swelling that subsides or goes away within 24 hours at one spot, but may appear in another spot, itching, and burning.
The mode of transmission can be allergies to food, dust, animal and insect bites, infections to illness such as the cold or the flu, exposure to Sun, stress, pressure on the skin or scratching, and contact with chemicals.
Dermotrographism is one of the most common types of uticaria or hives, in which the skin becomes raised or inflamed when stroked, scratched, rubbed, or sometimes even slapped. This is also known as skin writing.
Signs and symptoms include red, raised lines, swelling, infection, hive-like welts, and itching. There is no exact cause and the mode of transmission is not contagious.
This occurs mostly from rubbing of clothes or bed sheets.
Dementrographism may also proceed from an infection, stress, or medications such as penicillin.
Cholinergic Uticaria is four to six millimeter hives which develop after exposure to heat exercise or stress.
This is sometimes referred to as an exercise allergy.
Signs and symptoms include itching, burning, tingling, and warmth of the skin.
It may last minutes to hours; it is not contagious but exposure to Sun, heat, and exercise will increase the welts.
Cold Uticaria is hives which occur after exposure to cold.
Many occur after infections, medications, or emotional stress, and is most common in patients 18 to 25 years of age.
The signs and symptoms include hives, which usually develop within five minutes of exposure, and may last one to two hours after exposure to cold.
The mode of transmission is exposure to cold, but cold uticaria is not contagious.
Solar uticaria is hives that occur within minutes of being exposed to UV light.
This is also known as a Sun allergy.
Signs and symptoms include hives after exposure to Sun, which resolves within one to three hours.
The mode of transmission is exposure to UV light or the Sun.
Solar Uticaria is not contagious.
A sebaceous cyst is a closed sack under the skin that is filled with a cheesy like or oily material.
Signs and symptoms include a small, non painful lump beneath the skin.
This usually grows slowly and is not typically painful.
Warmth of the skin may occur in an infected area.
The cyst may have a grayish-white, cheesy, foul-smelling material that drains from the cyst.
Most commonly they are found on the face, neck, and trunk.
If the lump becomes infected or inflamed, other symptoms may include skin redness, and tender or sore skin.
The mode of transmission is not contagious, however, draining the sebaceous cyst is very important to prevent future infections.
Eczema is a generic term for a skin inflammation.
It affects 10-20% of infants and about 3% of adults.
Most infants outgrow this condition into adulthood.
Signs and symptoms include itchy skin.
Stress tends to cause the condition to worsen.
Modes are transmission include family history and other allergies or asthma.
Psoriasis is a skin redness and irritation. Most people have thick red skin with flaky, silver-white patches or scales.
Signs and symptoms can be acute or chronic; this includes scales and other symptoms may include general sores in males, joint pain or aching, nail changes, severe dandruff on the scalp, and is most often seen at the elbows, knees, and the middle of the body.
The mode of transmission is not contagious for psoriasis.
A melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer.
It is the leading cause of death from all skin diseases.
It can involve the colored part of the eye as well.
Signs and symptoms include a mole, sore, lump, or growth on the skin, a sore or growth that bleeds or changes in color.
The ABCDE system can help you remember the possible symptoms of a melanoma.
“A” stands for asymmetry: one half of the abnormal area is different from the other half.
“B” stands for border: the edges of the growth are irregular.
“C” stands for color: color changes from one area to another with shades of tan, brown, or black, or sometimes white, red, or blue; a mixture of colors may appear within one sore.
“D” stands for diameter: the spot is usually (but not always) larger than six millimeters in diameter, or about the size of a pencil eraser.
“E” stands for evolution: does the mole keep changing in appearance?
Melanomas are not contagious, and therefore have no mode of transmission.
Impetigo is a skin infection.
It is usually caused by the streptococcus or Staphylococcus bacteria.
It can also be caused by methicillin-resistant staph aureus or MRSA.
Signs and symptoms include blisters that are filled with pus and are easy to pop; they may be reddish or raw looking where a blister has broken; skin sores on the face, lips, arms, and legs spread to other areas; and swollen lymph nodes near the area of the infection.
For the mode of transmission, the skin normally has many types of bacteria.
The skin breaks, can allow bacteria in, and breaks in the skin can occur with animal bites, human bites, injury and other trauma to the skin, and insect bites.
Impetigo may also occur on the skin where there is no visible break.
It is most common in children who live in unhealthy conditions. In adult, it may occur following another skin problem, and may develop after a cold or another virus.
Impetigo can spread to others.
You can catch the infection if the fluid that oozes from the blisters touches an open area on your skin.
Cellulitis is a common skin infection caused by bacteria.
Signs and symptoms include fever, pain, or tenderness in the affected area, skin redness or inflammation that gets bigger as the infection spreads, skin sores or rash that grows quickly or suddenly in the first 24 hours, tight, glossy stretched appearance of the skin, warm skin in the area of redness.
There is no mode of transmission and cellulitis is not contagious. Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles; this is typically from a bacterial infection.
Common sites include the chest, face, axilla, buttocks, groin, and legs.
The S. aureus bacteria can occur when shaving with a razor blade.
Possible opening in the skin from nicks from shaving can allow the bacteria in. It can also be caused by friction as well.
There is no skin to skin transmission.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa or “hot tub folliculitis” is from a poorly maintained contaminated water.
There is no skin to skin transmission. Signs and symptoms of S. aureus are small, tender red papules or bumps which can occur in multiple areas.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is red, itchy papules most commonly under the areas covered by swimsuits.
Folliculitis is not contagious, and therefore does not have a mode of transmission.
Furunculosis is deeper in the hair follicle cavity.
The S aureus bacteria can contain strands of MRSA and can be difficult to treat.
A furuncle is a type of furunculosis that is similar to folliculitis, which is a boil or abscess containing pus that develops in a pre-existing site of folliculitis.
More commonly after puberty, these sites occur with trauma or friction at the waistline, beltline, axilla, groin, thighs, and buttocks.
A carbuncle is a type of furunculosis; it is a collection of several furuncles.
They are common among wrestlers and can be transmitted from skin to skin contact.
Signs and symptoms begin with tender, deep, firm, papula that enlarge and become painful.
They may fluctuate over a period of days.
Abscesses remain deep and reabsorb or drain through the skin.
Acne is a condition affecting the pilosebaceous unit that causes inflammatory lesions.
The appearance is red papules, pustules, or deep cysts.
They're typically non-inflammatory lesions (blackheads or whiteheads).
The transmission: acne is not considered contagious.
A paronychia is an infection affecting the proximal and lateral nail fold that separates the nail from the skin.
Signs and symptoms include bright red swelling in the folds of the tissue surrounding the nail.
Paronchias are not contagious, but if they are draining, personal protective equipment should be used.
An onychia is an infection of the nail matrix.
Signs and symptoms of an onychia include a purulent look underneath the nail.
It can also look like pus is underneath the nail.
Onychias are not contagious, but if draining is occurring, personal protective equipment should be used.
Herpes simplex is a viral infection.
It presents as cold sores, fever blisters, genital herpes, and herpes gladiatorum.
It is transmitted through skin that has been previously injured, such as cuts, abrasion, and damage.
Treatment includes oral antiviral medications including Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, Famciclovir.
Athletes should be withheld from sports until they are asymptomatic.
22% of people who are 12 or older are infected with a herpes simplex-2 virus.
80-90% of the population have herpes simplex-1 which is commonly chicken pox.
Signs and symptoms include flu-like symptoms, fever, sore throat, malaise, vesicles on the erythema--vesicles on the erythematous base, grouped vesicles in the same shape and age, tingling and pain occasionally, and they are usually reoccurring.
Varicella is also known as “chickenpox”.
It is a common childhood disease.
It is transmitted through respiratory droplets or skin to skin contact.
Patients are contagious two days before symptoms have appeared and until all lesions have crusted over.
Treatment includes lotions, antihistamines, and antibiotics for secondary bacterial infections.
Signs and symptoms include low grade fever, headache, malaise, papular vesicular rash, lesions will vary in size shape and age, and will rupture and form crust.
Varicella is extremely contagious and should be treated as such.
If an individual does not have chicken pox as a child but gets the disease in older age, this can actually turn into shingles, which can be very, very painful.
It is recommended for people who did not have chicken pox as a child that they get the shingles vaccination.
Herpes zoster is also known as shingles.
Shingles is a reaction of the herpes zoster virus involving the skin along the dermatomal distribution.
Shingles may occur as the result of advanced age, immunosuppression, lymphoma, stress, and radiation therapy.
Treatment includes high doses of medication that should be given within 72 hours of onset, narcotic analgesics, they should be withheld from play, physical activity, and physical contact with others until all lesions have crusted, so that they do not receive a secondary infection.
Signs and symptoms include pain, tingling, burning, and itching.
Symptoms may mimic myocardial infarction, pleurisy, acute abdominal pain, and migraine headache.
Patients may also have preceding outbreaks of fever, malaise, headache, and lymphadenopathy. Herpes zoster is extremely contagious, and therefore the mode of transmission is high.
Molluscum contangiousum is a disease of the skin and mucous membranes which is caused by the poxvirus.
Signs and symptoms are characterized by small, smooth, flesh-colored tone or white dome-shaped papules, with a central point.
They may be red, inflamed, or small and itchy.
The mode of transmission is spread by direct contact from person to person and through contaminated objects.
The human papillomavirus or HPV is a DNA virus.
It is an infection of the keratinocytes of the skin or mucous membranes.
Usually results in warts on the hands or feet.
There are 65 different types of the HPV virus.
Signs and symptoms include small smooth skin colored papules that may progress to a rough surface; they sometimes have a flat top surface.
The mode of transmission is skin to skin contact and can occur at sites that have trauma, abrasions, or eczema.
Taniya corpus is a common fungal infection characterized by scaly, erythematous lesions on the skin or ringworm.
Signs and symptoms are scaly areas that vary in size.
They may be itchy or they may be asymptomatic.
Mode of transmission is high, through skin-to-skin contact.
Tinea Cruris is also known as jock itch or ringworm of the groin.
It is an infection of the groin area caused by a fungus.
Signs and symptoms include red, raised, scaly patches that may blister or ooze.
Patches often have sharply defined edges.
Patches can be redder around the outside with normal skin tone on the center, and abnormally darker light-skinned.
Sometimes these changes in pigmentation are permanent.
The mode of transmission for tinea cruris can be triggered by friction from clothes or prolonged wetness in the groin area such as from sweating.
This can be passed from one person to the next by direct skin to skin contact or contact with unwashed clothing.
Tinea Unguium is often referred to as onychomycosis.
It is an infection of the nail tissue of the hands or feet.
There are possible seven signs and symptoms which include infected, thickened, cloudy, brittle, brown, lifted nails, and destruction of the tissue underneath the nails.
The mode of transmission for tinea unguium occurs by transmission of an infectious agent by one person to another through one or more of the following: saliva, air, coughing, fecal-oral route, surfaces, blood, needles, blood transfusion, sexual contact, or mother to fetus, among other modes of transmission.
Tinea Pedis is athlete's foot. It is an infection of the feet caused by a fungus.
Athletes foot may last for short or long time and may come back after treatment.
The most common symptom is cracked, flaking, peeling skin between the toes are on the side of the foot.
It may also include red and itchy skin, burning or stinging pain, blisters that ooze or get crusty, and if the fungus spreads to the nails, they can become discolored, thick and even decay.
Athletes foot may occur at the same time as other fungal skin infections such as jock itch.
Athletes foot is the most common type of tinea fungal infection.
The fungus thrives in warm moist areas.
Athletes foot is easily spread and can be passed through direct contact or contact with items such as shoes, stockings, and the shower or pool surfaces.
Tinea capitis is a fungal infection of the scalp.
This is also called ringworm of the scalp.
Signs and symptoms include bald patches with small black dots due to hair that is broken off, scaly areas of the skin that are red and swollen, pus-filled sores called kerions, low-grade fever around 100 swollen lymph nodes, itchy scalp.
The modes of transmission or causes are most likely mold-like fungi called dermatophytes.
The fungi grow well in warm, moist areas.
It is not uncommon to have minor skin or scalp injuries.
This can also happen in people who do not like to bathe like teenagers.
It can also occur if you have a wet scalp for long periods of time or a sweaty scalp for long periods of time.
Tinea Veriscolor is a fungal infection of the skin. It is caused by the type of yeast that naturally lives on your skin.
When the yeast grows out of control, the skin disease, which appears as a rash, is the result.
Signs and symptoms include patches that may be white, pink, red, or brown, and can be lighter or darker than the skin around them, areas that do not tan, most commonly seen on the neck, arms, and hands.
Modes of transmission or causes can include if you have oily skin, hotter climate, if you're sweating a lot, if you have a weak immune system, basically if you live in Corpus Christi you have a higher risk, it's not contagious, and it usually affects teens and adults.
Head lice are parasites that are found on the human head.
They are spread by person-to-person contact or the sharing of combs, brushes, caps, and other clothing.
They are with preschool and schoolchildren. Up to 1 in every 10 children in school acquires head lice at some point.
Signs and symptoms include tickling or feeling like something is moving through the hair, itching caused by an allergic reaction to the bites, sores on the head, sores on the head can sometimes become infected.
The mode of transmission is contact with an already infested person, wearing infested clothing, and head lice are most frequently located on the scalp, behind the ears, near the neckline at the back of the neck.
Body and pubic lice are blood sucking insects.
Lice are 3 millimeters long, they have three pairs of legs the end and powerful claws.
Females live for one two three months and can lay up to 300 eggs. Three species of lice have adapted to live on humans.
Head louse, crabs, and body or pubic lice.
Signs and symptoms include diagnosis that is based on finding adult lice or eggs, red itchy papules or itching that is worse at night, blue macules may be visible at the feeding sites, minute dark brown specks of lice excreta, or lice poop are sometimes seen in the skin and underwear.
Modes of transmission is person-to-person contact. Scabies are an infestation of the skin by a human itch mite.
Microscopic scabies mites burrow into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays eggs.
Signs and symptoms include intense itching, pimple-like skin rash, and the mode of transmission is direct prolonged skin to skin contact with a person who has scabies.
Chigger bites are tiny members of the arachnoid family--you probably won't see them.
However, their bites pack a powerful punch.
Signs and symptoms include intense itching and the desire to scratch.
Bites can appear in clusters and can form a rash.
Sugar bytes in the male genitalia can cause severe itching, swelling, and painful urination.
Modes of transmission: chiggers live in tall weeds and grass, sometimes in berry patches in wooded areas.
These chiggers quickly attach to your skin if you walk by or brush up against vegetation. They are temperature sensitive, so if the temperature is below 60° Fahrenheit, the chiggers become inactive.
If it's below 42° Fahrenheit, chiggers die.
We can see that chiggers live mostly in the southern part of the United States; Texas is among that.
A leukoplakia or keratosis are thick and white patches.
They form on the gums, inside the cheeks, at the bottom of the mouth, and tongue.
Patches cannot be scraped off.
Signs and symptoms include white or grayish in patches that can't be easily wiped away.
They may be irregular or flattened texture, thickened or hardened in areas, they may also be associated with red, raised lesions or erthroplakia, which is more likely to show precancerous changes.
The cause of leukoplakia is unknown.
Tobacco use including smoking and chewing appears to be responsible for most cases.
Squamous cell carcinoma is a common form of skin cancer.
It develops in the thin flat squamous cells at the outer layer of the skin.
Signs and symptoms include a firm red nodule, a flat red sore with scaly crusts, a new sore or raised area on an old scar or ulcer, a rough scaly patch near lip that may evolve to an open sore, a red sore or rough patch inside your mouth, a red raised patch or wart-likes or in or on the anus or on your genitals.
The mode of transmission is prolonged exposure to UV or ultraviolet radiation, most commonly from sunlight, or tanning beds, or lamps.
Kaposi’s Sarcoma is a cancerous tumor on the connective tissue.
It is often associated with AIDS.
Signs and symptoms include a blue-red or purple bumps on the skin, which are rich in blood vessels.
Lesions may first appear on the feet, ankles, thighs, arms, hands, or face.
Other symptoms may include bloody sputum, shortness of breath.
Modes of transmission in people with AIDS, Kaposi's sarcoma is most commonly caused by an interaction between HIV, a weakened immune system, and the human herpesvirus -8 or HHV-8.
Kaposi sarcoma has been linked to the spread of HIV and HHV-8 through sexual activity.
.
As found on Youtube